Feed Mapping
The Feed mapping type allows you to sub-sample rectangular areas in a content area (referred to as the Mapping canvas) and copy that content onto rectangles inside one or multiple screens.
Feed mapping lets you specify any number of source rectangles within your content and map them individually to multiple surfaces. With Feed mapping, all your screens can easily be turned into one overall raster, and content applied to each surface with pixel-perfect accuracy. Individually move, scale, crop, chop or flip your source rectangles to compensate for differences in pixel density or to create interesting mapping effects.
-
In your track, create a new visual layer. These layer types can include content layers, generative layers, and effect layers.
-
Left click on the layer in the track to open the Layer Editor on the left side of the GUI.
-
Under the Default tab, left click on the Mapping parameter to display a list of the mappings in the project.
-
A manager titled mappings will appear – this is a list of all mappings within your project. By default, all screens will be populated with a direct mapping sharing the same name, and all cameras will be populated with a perspective mapping sharing the same name.
-
Type directly into the New mapping: text field to create a new mapping. A list will appear prompting to you select the mapping type.
-
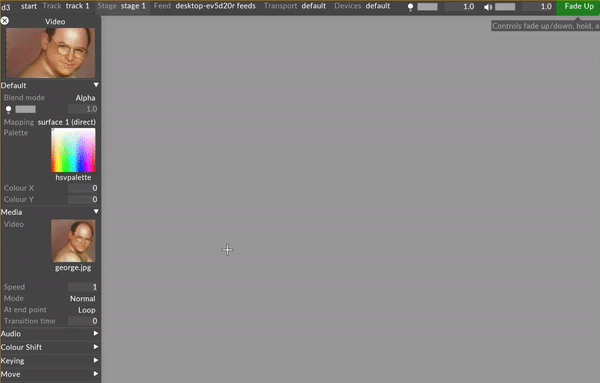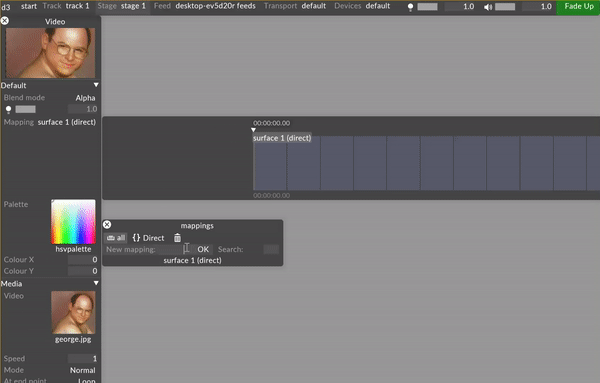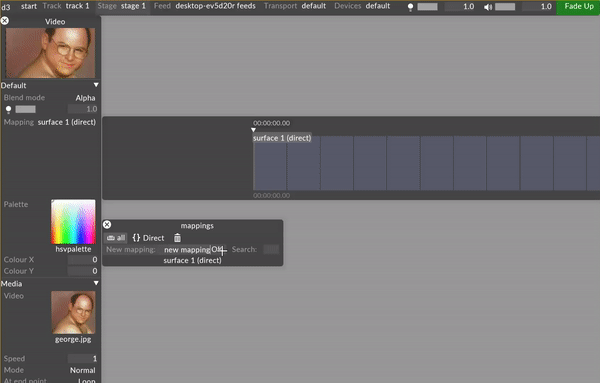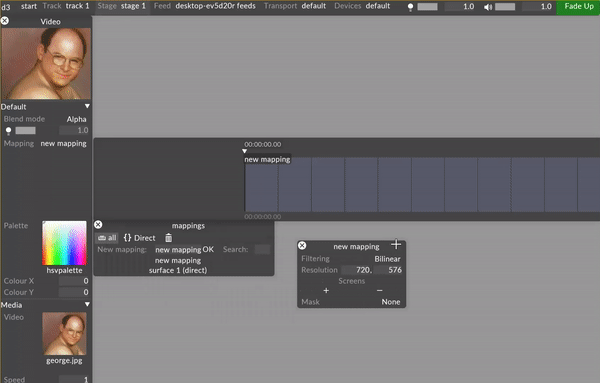
An editor with the user assigned name of the mapping will appear once a mapping type is selected.
-
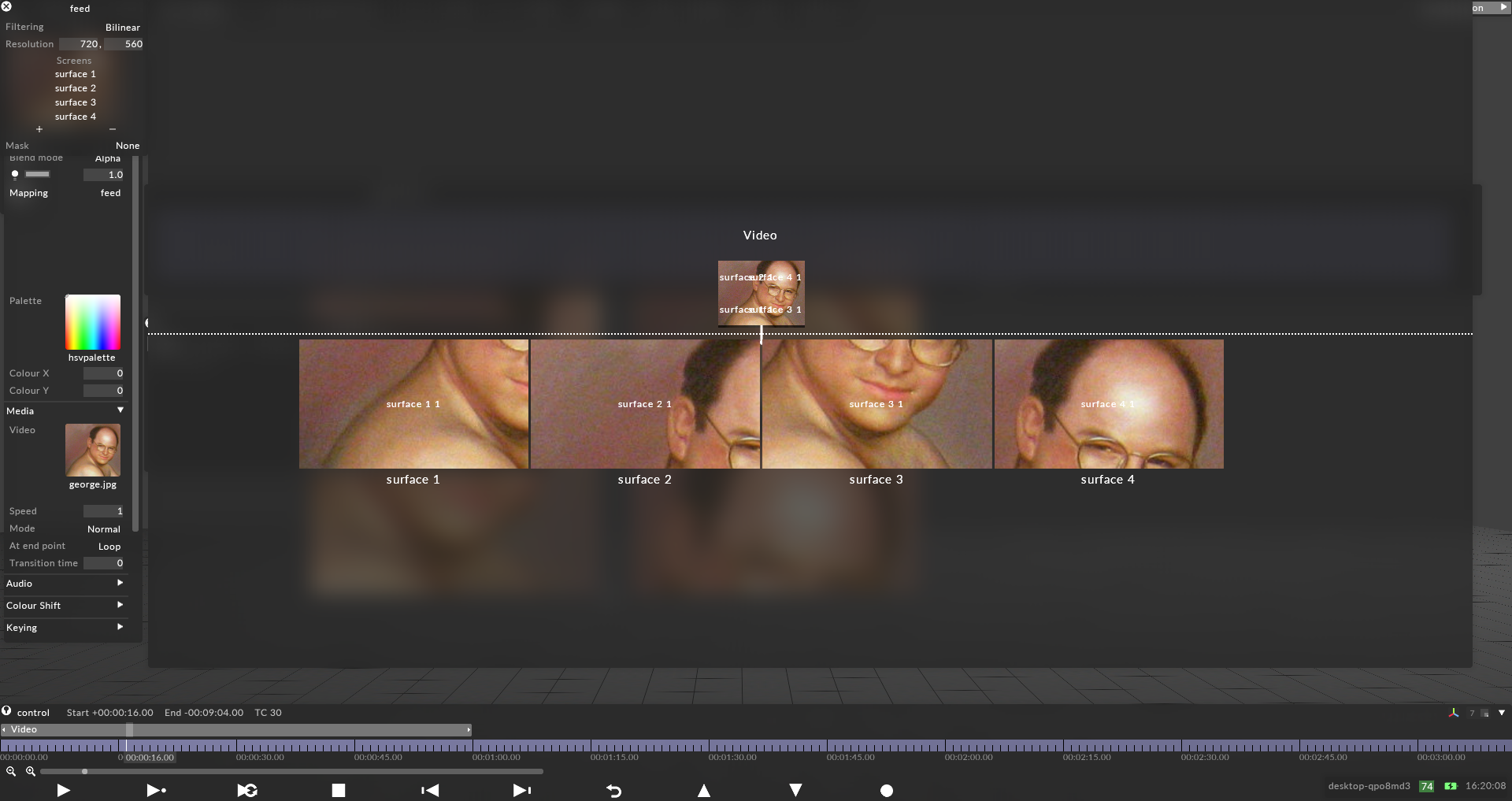
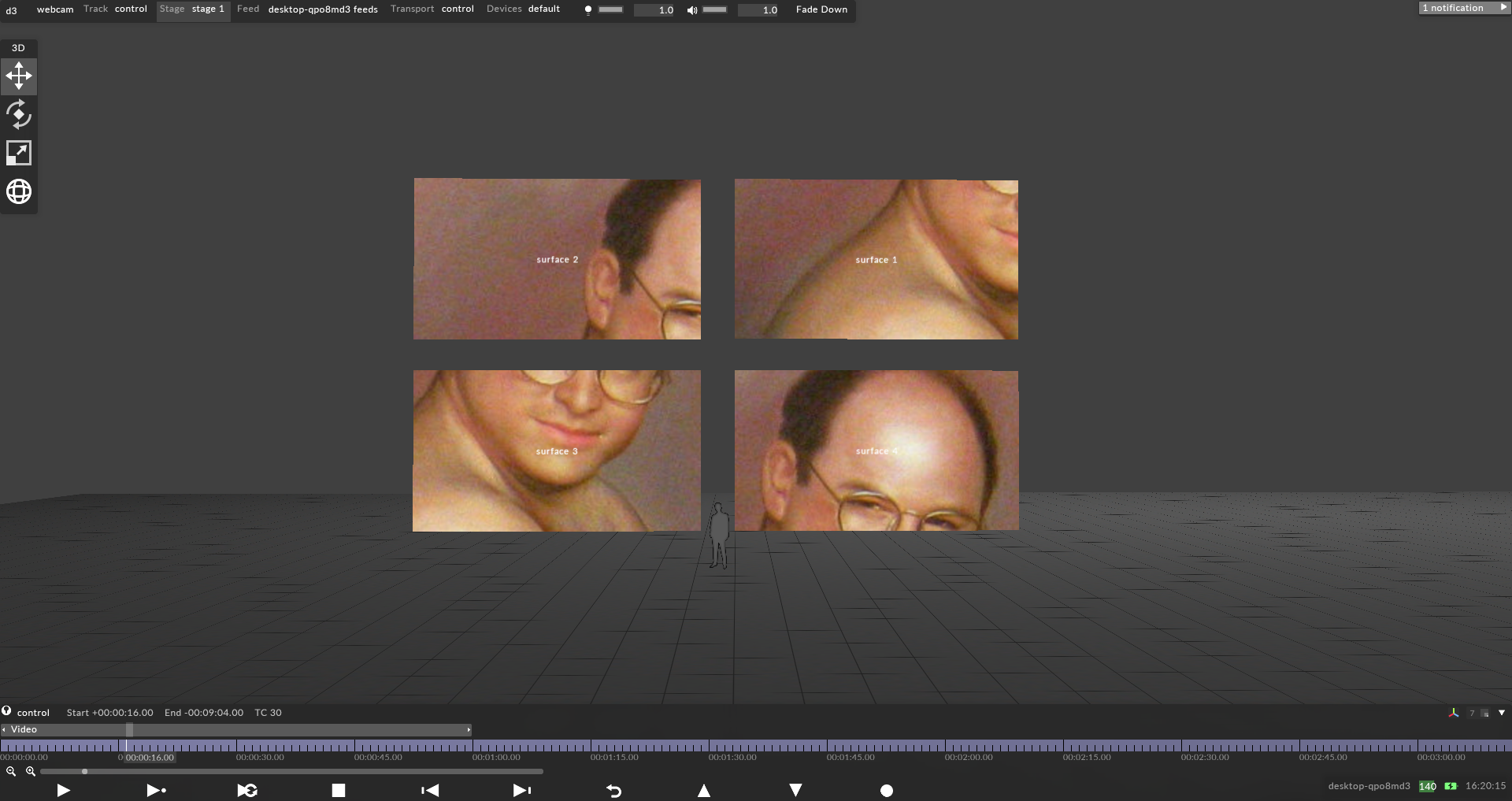
Assign all screens that will be used for the mapping and enter the resolution of the content that will be displayed on the screens.
-
Edit the specific properties of the chosen mapping type.
-
Assign a piece of content to the layer in the track, and the content will be displayed on the assigned screens of the mapping in the stage and the feed output window.
This section explains the properties that are shared by the six different mapping types.
Filtering
Nearest - Nearest neighbor filtering. Use nearest-neigbour sampling, to disable blending between pixels when scaling. Can be used to create pixellated looks, or to ensure hard edges on certain types of content.
Bilinear - Bilinear filtering is a texture filtering method used to smooth textures when displayed larger or smaller than they actually are.
2x Multi-sample - Multi-Sample filtering can help fix issues with scaled content, but can introduce some blurriness.
Resolution
This controls the canvas size the layer renders into, in pixels. The Direct mapping type starts with a 256x256 pixel canvas and automatically sets the canvas size to that of the first screen you add.
Screens
This is a list of screens that the selected mapping type can copy content to.
-
Left-click + to open the Screens manager.
-
Left-click the Screens you want to map. This will copy the individual canvas content onto these three Screens simultaneously and will add the Screen names to the mapping object editor.
-
Left-click and drag the Screens listed in the mapping object editor to -. This will remove the canvas content from the Screens and delete the Screen names from the mapping object editor.
Mask
This points to the Texture file that defines a Mask bitmap. You can use this property to apply a Mask bitmap to the mapping canvas. Selecting this property will open the Texture object library, which shows all of the still image files saved on your local hard-drive in the DxTexture folder.
To apply a mapping mask you will need to create and import a custom still image file.
-
The step-by-step instructions on how to create and import a custom Population mask can be used to create a custom mapping mask. The only difference is that the mapping masks resolution should be the same as the mapping canvas. For step-by-step instructions on how to create and import a Population mask into a d3 project visit to the section Population mask in the Editing screens sub-chapter.
-
Alternatively, set any layers blend mode to mask to channel the layer content into the mapping mask.
In addition to the property explanations provided in the sub-chapter Common mapping type properties, it is important to:
-
Set the resolution of the Feed mapping to the same resolution as the content intended to be used for that Feed mapping. If the content is of a higher resolution than the resolution of the Feed mapping mapping canvas, Disguise software will by default crop away the sides of the content. If the content is of lower resolution, Disguise software will scale up the content inside the mapping canvas.
-
Add the screens to the Feed mapping in the same order as they appear in the visualiser, from left to right. If the screens are not listed in that order yet, you can re-order the screens in the screens list by selecting and dragging a screen up or down.
To add a Feed rectangle to the mapping canvas:
-
Right-click the red screen canvas and select Add feed rectangle .
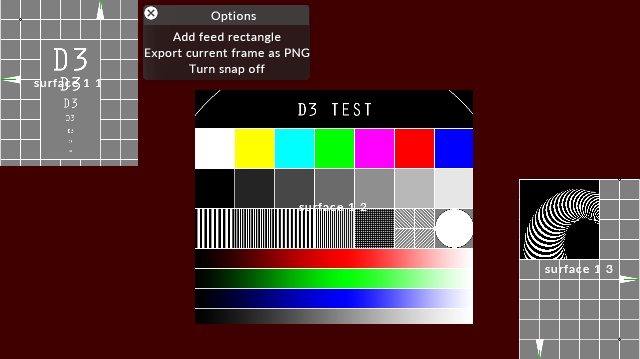
View of the Feed mapping editor when adding a new Feed rectangle
Note that the Feed rectangle is by default positioned in the top left corner of the mapping canvas. To change the position of the Feed rectangle, left-click it once, place the cursor in the middle and start moving it.
The Feed rectangle has a number of options for scaling, flipping and chopping the rectangle. These options are very similar to those used when editing a Feed rectangle in the Output Feeds level. For more information please see the sub-chapter Quick editing controls.
This image explains the various options associated with a Feed rectangle in the Stage level.
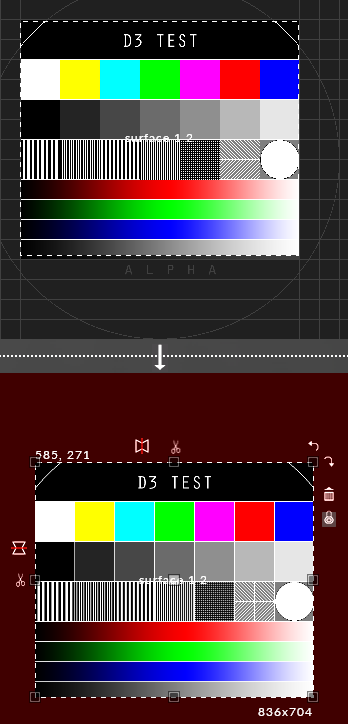
Feed rectangle quick editing controls
| Item | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
The position of the sample rectangle placed on the Mapping Canvas, in pixels |

|
The Scissor tool on the sample rectangle for vertical cuts. Left-click and hold down the mouse button to move the cut horizontally. |

|
The Scissor tool on the sample rectangle for horizontal cuts. Left-click and hold down the mouse button to move the cut vertically. |

|
The Bin . Left-click the bin icon once to delete the sample rectangle (and the Feed rectangle). |

|
The size of the sample rectangle in pixels. |

|
The Flipping tool to flip the sample rectangle horizontally. |

|
The Scissor tool on the Feed rectangle for vertical cuts. Left-click and hold down the mouse button to move the cut horizontally. |
|
The Rotate tool on the Feed rectangle for rotating the Feed rectangle 90 degree clock/anti-clockwise. |

|
The Scissor tool on the Feed rectangle for horizontal cuts. Left-click and hold down the mouse button to move the cut vertically. |

|
The Flipping tool to flip the sample rectangle vertically. |

|
The Bin . Left-click the bin icon once to delete the Feed rectangle (and the sample rectangle). |

|
The Lock button locks the size of the sample rectangle to the size of the Feed rectangle and vice versa. Left-click the Lock button once to unlock the dependency. |

|
The name of the screen. |

|
The size of the Feed rectangle in pixels. |
Using these tools gives you a lot of freedom for configuring the Feed mapping on the screens in the Stage. Below, you can see an extreme example of this (for demonstration purposes only). Note that the red color in the background on the left hand side will only show up if the Feed mapping editor is open. When closed, the background will remain black.
Right clicking a feed rectangle offers the following properties.
Add feed rectangle
This option adds another feed rectangle to the canvas.
Export current frame as PNG
A PNG of the feed rectangle is exported to the screenshots folder of your project folder. For more information see project structure.
Edit feed warping
This option allows you to draw a 2D warp on an individual feed rectangle. Usful for warping within the mapping layer as oppose to the feed level.
Select mask
This option allows you to add a mask to the feed rectangle. Masks are read from the DxTexture folder of your Objects folder within your project folder. For more information see project structure.
Duplicate
This allows you to create a duplicate of the feed rectangle.
Duplicate multiple
This allows you to duplicated multiple source and destination feed rectangles to create arrays of feed rectangles within the mapping.
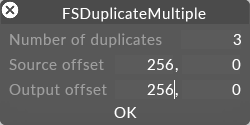
The duplicate multiple editor.
Turn snap off
This option toggles feed rectangle snapping on and off. When on, feed rectangle edges will snap to one another, and when off they do not do this (note the rulers still show with snapping off).
The easiest way to import and export feed maps from projects is via a table. A feed map can be exported to a text file from Disguise software and then imported to another project.
Export
-
In your feedmap, right click and choose Export to table.
-
Enter a name
-
Hit OK
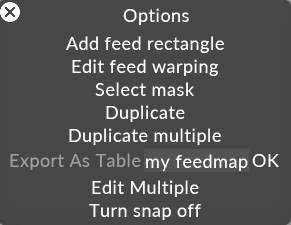
-
The feed map is now exported to a newly created table folder in the objects folder.
The table that is exported will look similar to this example:
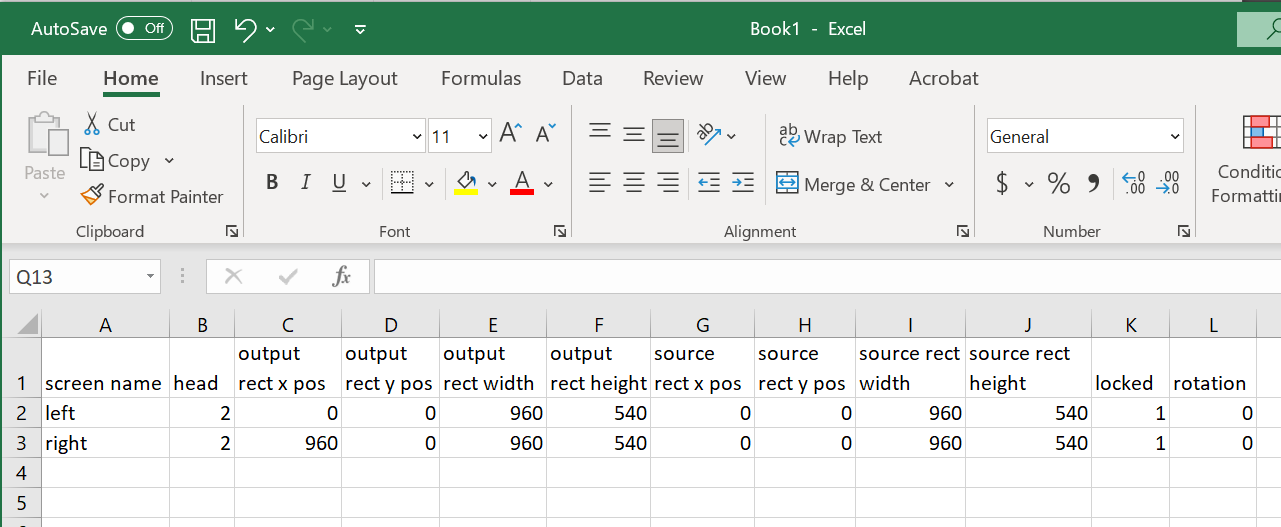
"Screen Name" refers to the name of the feed rectangle while "Head" refers to the number of the output slot.
Import
-
In your new project, create a feed mapping. The mapping does not need to share the same name as the one you are importing.
-
Left click the Import from table option, this will only appear if there is a table folder present in the project folder.
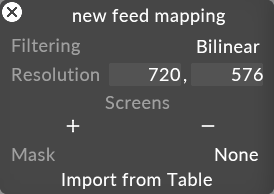
-
Left click your table from the available list.

-
Choose yes when prompted to overwrite existing feed rectangles.